South America
Columbia - Since 1995, IRT has been assisting in updating and constructing compositional, full field models, using VIP and Eclipse, becoming the basic tool for planning future depletion strategies for the client. Projects have included two of the largest fields in Colombia (Cupiagua and Cusiana), Portions of this work have been performed at the client's facility in Colombia, including technology transfer and training.
Cupiagua Field, Colombia, Ecopetrol / BP
International Reservoir Technologies has performed a series of integrated studies of the giant Cupiagua gas condensate reservoir in order to estimate reserves, define infill and step-out drilling locations, and provide a complete evaluation of development and surface equipment scenarios. In these studies, the complex structural geology of the field was defined through the detailed interpretation of approximately thirty 2-D seismic lines, which were tied in time, phase, amplitude and frequency to form a consistent data set. Interpretation was performed with the Landmark SeisWorks program and was validated through the construction of balanced structural cross-sections in the Cogniseis Geosec package. All cores in the field were described in detail and were integrated into the reservoir description through stratigraphic cross-sections and property maps.
This information was all incorporated into a compositional full field model of the reservoir using the Landmark VIP software suite. The model was based on analyses of several PVT tests for different wells that indicated the reservoir fluid to be a near-critical point fluid with significant compositional variations with depth and temperature. These PVT anomalies were all successfully modeled and incorporated into the full field model. The compositional modeling work was used to test fourteen different development scenarios in terms of ultimate recovery and production rate over time, including several miscible gas displacement scenarios.
IRT continues to be involved in model studies of Cupiagua and satellite reservoirs in support of field development efforts.
Cusiana Field, Colombia; Ecopetrol / BP
International Reservoir Technologies performed an integrated review of reservoir model of the giant Cusiana Field. In this study, the work of a foreign operator in planning the reservoir depletion was reviewed for ECOPETROL. The work by the operator included a detailed reservoir description, a major simulation model, and detailed operating strategies. Findings from the study assisted ECOPETROL in guiding and understanding these strategies, as well as providing important refinements.
IRT assisted ECOPETROL in the construction of a new compositional full field model of the Cusiana Field using VIP. This model is now the basic tool for planning future depletion strategies for ECOPETROL. Part of the effort included technology transfer and training. Portions of this work are performed on-site in Bogot.
IRT continues to be involved in model studies of the Cusiana Reservoir in the support offield development efforts.
El Segundo Field, Colombia; Ecopetrol / Sipetrol
The reservoir exists in a regional syncline with a local anticlinal development. In these studies, the complex structural geology of the field was defined through the detailed interpretation of 2-D and 3-D seismic with statistical curvature analysis of dip meter data. All cores in the field were described in detail and were integrated into the reservoir description. Stratigraphic analysis identified nine separate facies within the productive reservoir horizon. Extensive petrophysical data, including FMI logs and over 300 thin-section analyses were integrated with engineering data to show that the highly productive reservoir likely consisted of fractures only with no effective matrix porosity.
**Study updated 2003-2004 for the operator, SIPETROL, under the revised field name, Guaduas.
Floreña Field, Colombia; Ecopetrol / Sipetrol
In August of 1998, International Reservoir Technologies, Inc. was contracted to perform a simulation study of the Floreña Field defining sensitivity cases to evaluate principal recovery factors of a gas injection project in a volatile oil field. The study utilized existing reports / data and worked in concert with the client and the Colombian Institute of Petroleum. Three scenarios were developed for OOIP with an evaluation of various recovery possibilities using the simulation model to provide forecasts suitable for economic evaluation of each scenario.
Contact our office  for additional information. 303-279-0877
for additional information. 303-279-0877
Venezuela - Since 1994, IRT has has conducted various integrated studies in this highly complex geologic environment. Each study utilizes an integrated team of multidisciplinary professionals and is contracted over a multi year period. IRT continues to identify short term opportunities and optimize long term development plans for our clients.
Bachaquero, Lake Maracaibo, Venezuela; PDVSA
Bach-01 field is a heavy oil sand in the Lagunillas-Lago unit of the Tía Juana District. The field has produced over 420 million barrels from 641 wells. There are numerous horizontal wells and over 1000 steam cycles into 350 wells. The Bach-01 Field was put on production in August 1934 with the completion of the LL-231 well in the area operated by the Former Lagoven, and the field has had continuous production for over 75 years. Both solution gas and compaction (subsidence) have been important recovery mechanisms in the field. Recovery is about 6% of the estimated 6600 MMstb POES. IRT is evaluating future recovery strategies including continuous steam injection (ICV) and steam assisted gravity drainage (SAGD), among other technologically available alternatives. IRT is performing a full-integrated study of the field including development of a digital database, complete reservoir description, construction of a 3D geological static model with associated rock properties, oil-water contact definition, reserves, and reservoir simulation.
Contact our office  for additional information
. 303-279-0877
for additional information
. 303-279-0877
C2/VLE305, Lake Maracaibo, Venezuela; PDVSA
C2/VLE305 is a highly complex reservoir both structurally and stratigraphically. International Reservoir Technologies utilized an existing geological static model and constructed a 3D geocellular model for geostatistical analysis of the field. A geocellular model was then used for reservoir simulation involving history matching, water flood optimization and analysis of WAG. Petrophysical review resulted in recomputation of v-shale values and effective porosities. Errors in structural interpretation at the faults were corrected with the aid of the interpreted seismic data and then modified horizons for each of the C2 sand flow units were entered into a new IRMS geological model. Predominate facies were mapped deterministically and combined with IRMS software based facies object modeling as a basis for the geostatistical determination of net-to-gross, porosities, and permeabilities for each of 319 layers. A 34 layer simulation model of the area was built and history match developed. The field has produced over 300 million barrels from the Eocene Misoa sands. The reservoir has 138 wells and about 1500 MMstb POES.
Contact our office  for additional information
. 303-279-0877
for additional information
. 303-279-0877
VLE196/VLE460, Lake Maracaibo, Venezuela; PDVSA
In November 2000 PDVSA contacted International Reservoir Technologies, Inc to conduct a reservoir simulation study of the VLE196 and VLE460 areas in Lake Maracaibo, Venezuela. The goals of this study were to provide an updated geologic description for four (4) reservoirs, quantify OOIP and reserves, identify opportunities to increase oil production and locate additional reserves and recommend improved recovery techniques to maximize the field's potential within these reservoirs.
The study was a corroborative effort between IRT and PDVSA staff members. A new geologic model was constructed that ties VLE196/VLE460 to Block VI Lamar, Block VI East and Block V Centro, thereby creating an internally consistent framework. This model is tightly integrated between seismic, well logs, core date, oil-water contacts, pressure tests and production data.
A 3D full-field reservoir simulation model has been history-matched to pressure and production performance. Many late time wells have found small compartments of bypassed oil that present a challenge for the history match. Fault sealing (and opening) was a key variable required to reach a match. Faults in the study area are not completely open or completely closed. Facies transition from one type to another was found to create compartments.
In conclusion, after 20 years, large areas were left unswept by existing wells, workovers and recompletions. To access the remaining oil, several drilling opportunities, recompletions and/or waterflooding were Identified or future evaluation by PDVSA., with an estimated ultimate recovery of 78% of the proven MOOIP and 44% of the proven OOIP.
Contact our office  for additional information
. 303-279-0877
for additional information
. 303-279-0877
Block V Centro & VI East, Lake Maracaibo, Venezuela; PDVSA
Block V Centro is a highly complex field both structurally and stratigraphically. The field has produced over 300 million barrels from the Eocene Misoa sands. The study included 260 wells and Block V Centro has a POES of about 1500 MMstb. International Reservoir Technologies performed a fully integrated study of the Block V Centro field. The reservoir description included interpretation of 225 km2 of 3D seismic, detailed correlation of 44 flow units based on sequence stratigraphic and genetic stratigraphic concepts within the 260 wells penetrating the Misoa B and C sands. Core description was used to associate depositional facies with log signature. Within a single stratigraphic unit, log signature was correlated between wells to provide an areal distribution of facies. Petrophysical analysis was performed on 61 wells calibrated to core measurements and previous petrophysical analysis. Facies are assigned unique rock properties based on the petrophysical analysis, thus representing the lateral heterogeneity within a single stratigraphic layer.
Contact our office  for additional information.
303-279-0877
for additional information.
303-279-0877
Lamar Block VI Field, Lake Maracaibo, Venezuela; PDVSA
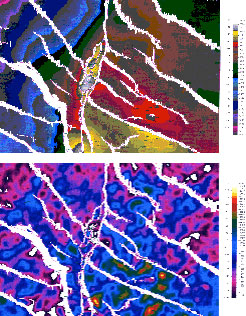 Lamar Block VI is a highly complex reservoir both structurally and stratigraphically. The field has produced over 300 million barrels from the Eocene Misoa sands. For this integrated study, International Reservoir Technologies first provided a detailed description of all available cores, identifying key sequence stratigraphic surfaces, systems tracts, and depositional facies. International Reservoir Technologies performed a detailed 3-D seismic interpretation over the block using the Landmark SeisWorks software, integrating the interpretation with abundant dipmeter data for fault and fold geometry control, well log picks, and production data. Wavelet extraction was performed to provide an understanding of the phase and frequency content of the data, and the results were used in generating synthetic seismograms to tie well log picks to the seismic volume. Seven horizons have now been mapped in time and depth, and these maps have been used as the basis for identifying fifteen step-out and infill drilling prospects. International Reservoir Technologies has built a detailed reservoir model of Block VI with 44 flow units and 40 major faults. Seismic attribute analysis and forward modeling has been performed to determine the nature of amplitude anomalies apparent in the data set. These were used as guides for reservoir mapping, and in determining current fluid contacts or pressure compartments. The reservoir model contains in excess of 100,000 grid cells and the simulation is being performed with the Schlumberger GeoQuest Eclipse simulation system. The model was history matched and is now being used to predict the behavior of planned infill drilling and water injection projects in the Block.
Lamar Block VI is a highly complex reservoir both structurally and stratigraphically. The field has produced over 300 million barrels from the Eocene Misoa sands. For this integrated study, International Reservoir Technologies first provided a detailed description of all available cores, identifying key sequence stratigraphic surfaces, systems tracts, and depositional facies. International Reservoir Technologies performed a detailed 3-D seismic interpretation over the block using the Landmark SeisWorks software, integrating the interpretation with abundant dipmeter data for fault and fold geometry control, well log picks, and production data. Wavelet extraction was performed to provide an understanding of the phase and frequency content of the data, and the results were used in generating synthetic seismograms to tie well log picks to the seismic volume. Seven horizons have now been mapped in time and depth, and these maps have been used as the basis for identifying fifteen step-out and infill drilling prospects. International Reservoir Technologies has built a detailed reservoir model of Block VI with 44 flow units and 40 major faults. Seismic attribute analysis and forward modeling has been performed to determine the nature of amplitude anomalies apparent in the data set. These were used as guides for reservoir mapping, and in determining current fluid contacts or pressure compartments. The reservoir model contains in excess of 100,000 grid cells and the simulation is being performed with the Schlumberger GeoQuest Eclipse simulation system. The model was history matched and is now being used to predict the behavior of planned infill drilling and water injection projects in the Block.
Contact our office  for additional information
. 303-279-0877
for additional information
. 303-279-0877